Jobsheet 5 - Conditional Syntax 1
Operator
Operator is special symbols that used to operate data (operand). Kind of operator is Assignment Operator, Arithmatic Operator, Relational Operator and Logical Operator.
Assignment Operator
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
= |
Set value from right operand into left operand | C = A means set A's value into C |
+= |
Add left operand with right operand and set value into left operand | C += A equals C = C + A |
-= |
Subtract left operand with right operand and set value into left operand | C -= A equals C = C - A |
*= |
Multiply left operand with right operand and set value into left operand | C *= A equals C = C * A |
/= |
Divide left operand with right operand and set value into left operand | C /= A equals C = C / A |
%= |
Run modulo operation left operand with right operand and set value into left operand | C %= A equals C = C % A |
Arithmatic Operator (Binary and Unary)
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
+ |
Plus operator |
- |
Subtract operator |
* |
Multiply operator |
/ |
Divide operator |
% |
Modulo operator |
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
++ |
increase one value (increment) |
-- |
decrease one value (decreement) |
Relational Operator
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
== |
equals operator, return true if the condition is equals |
!= |
not equals operator |
> |
greater than operator |
< |
less than operator |
>= |
greater than or equals operator |
<= |
less than or equals operator |
Logical Operator
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
&& |
And operator |
|| |
Or operator |
! |
Not operator |
Basic Conditional Syntax
if
if (condition) {
statement;
statement;
}
Example
import java.util.Scanner;
public class IfSyntax {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Please input temperature: ");
int temperature = sc.nextInt();
if (temperature < 16) {
System.out.println("Please wear your jacket!");
}
}
}
Output

if-else
if (condition) {
statement;
statement;
} else {
statement;
}
Example
import java.util.Scanner;
public class IfElseSyntax {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Please input temperature: ");
int temperature = sc.nextInt();
if (temperature < 16) {
System.out.println("Please wear your jacket!");
} else {
System.out.println("Please wear your cap!");
}
}
}
Output

switch-case
switch (condition) {
case constant-1:
statement;
break;
case constant-2:
statement-2;
break;
...
...
case constant-n:
statement-n;
break;
default:
statement;
}
Example
import java.util.Scanner;
public class SwitchCaseSyntax {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Input the number: ");
int number = sc.nextInt();
switch (number) {
case 1:
System.out.println("It's Sunday");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("It's Monday");
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("It's Tuesday");
break;
case 4:
System.out.println("It's Wednesday");
break;
case 5:
System.out.println("It's Thursday");
break;
case 6:
System.out.println("It's Friday");
break;
case 7:
System.out.println("It's Saturday");
break;
default:
System.out.println("Your number is invalid!");
}
}
}
Output

Multiple Conditional Syntax
Experiment
Experiment 1
- Open your text editor (Sublime, Notepad++, VSCode or Atom)
- Create new file then give filename
Number.java - Create class
Number - Write
main()function java Add external library
Scannerimport java.util.Scanner;Declare variable with name
scannerand datatype isScannerScanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);Create a variable with datatype integer, then give name
number.int number;Then insert code below to receive input from user.
System.out.print("Please input the number: "); number = scanner.nextInt();Create conditional structure to check the number is even or odd. We can use the remaining values from modulus by 2.
if (number % 2 == 0) { System.out.println("Number " + number + " is even."); } else { System.out.println("Number " + number + " is odd."); }- Compile the java file using
javaccommand, then execute the program.
Experiment 2
- Open text editor (sublime, VSCode, Notepad++ or Atom)
See the picture below!
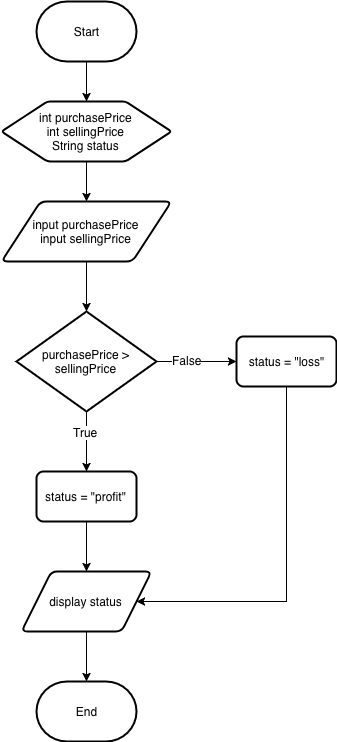
Create filename with name
ProfitOrLoss.java- Then create class with name
ProfitOrLoss - Write basic structure
main()function - Add import library
Scannerimport java.util.Scanner; - Declare variable
scwith datatypeScannerScanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); Create two variables with datatype
intand a variableString.int purchasePrice; int sellingPrice; String status = null;Insert code below to ask user input.
System.out.print("Please input the purchase price: "); purchasePrice = sc.nextInt(); System.out.print("Please input the selling price: "); sellingPrice = sc.nextInt();Create basic structure conditional to check profit or loss.
if (sellingPrice > purchasePrice) { status = "Profit"; } else { status = "Loss"; }Add code below to display the output of status
System.out.println("You're " + status);Compile using
javacand then run the program!
Experiment 3
- Open text editor (Sublime, VSCode, Notepad++ or Atom)
- Create new filename
Calculator.java - Create classname
Calculator - Write basic
main()function - Add import library
Scannerimport java.util.Scanner; - Declare
scasScanner Create three variables with data type double and a variable with data type char. Then give the names as
number1,number2,resultandoperator.double number1, number2, number3; char operator;- Add code below to ask user input.
System.out.print("Input first number: "); number1 = sc.nextDouble(); System.out.print("Input second number: "); number2 = sc.nextDouble(); System.out.print("Input operator (+ - * /): "); operator = sc.next().charAt(0); Create
switch-caseto calculate operation.switch (operator) { case '+': result = number1 + number2; System.out.println(number1 + " + " + number2 + " = " + result); break; case '-': result = number1 - number2; System.out.println(number1 + " - " + number2 + " = " + result); break; case '*': result = number1 * number2; System.out.println(number1 + " * " + number2 + " = " + result); break; case '/': result = number1 / number2; System.out.println(number1 + " / " + number2 + " = " + result); break; default: System.out.println("Wrong operator!"); }- Compile and execute the program!
Questions
Explain the purpose of keyword below!
elsebreakdefault
Explain the purpose of syntax below:
operator = sc.next().charAt(0);if (number % 2 == 0)
In the experiment 3 add feature to calculate remaining value using modulus operator
%!
Assignment
Create the program that needs input two integer number, then display the max number into the screen!
Please see the picture of flowchart below!
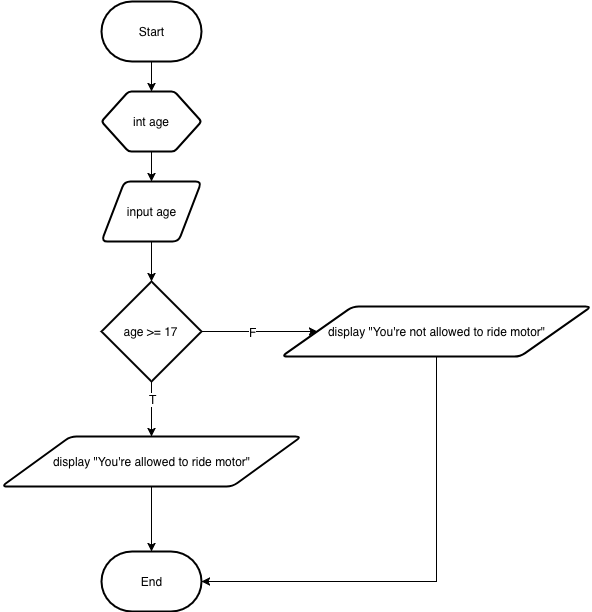
Create the program based on the flowchart!
Financial officer calculate salary of employees every end of month. Total salary based on basic pay, meal allowance, and transportation allowance.
Total salary = basic pay + meal allowance + transportation allowanceIf the total salary received is more than equal to IDR 1.500.000,00 then the salary is cut by tax 5%, while employees with total salary below IDR 1.500.000,00 do not get tax. Create the program to help financial officer calculate the total salary!
Create the program to determine placement class of student. If the grade of midterm exam more than 90 or the grade of final exam is equals 100, then the student go to class A, other than that go to class B. (Input: name of student, grade midterm exam and grade final exam!).